For people with severe lung disease, a lung transplant can be a life-saving treatment. Unfortunately, not all patients who need a new pair of lungs will receive them: the demand for healthy lungs far exceeds availability.
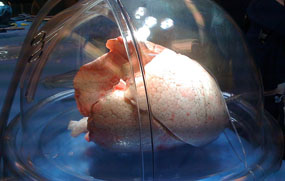
To increase the number of lungs suitable for transplantation, TGHRI Senior Scientist Dr. Shaf Keshavjee and his team developed a new technique that better preserves the lung during its transit from the donor to recipient. The technique —known as ex vivo lung perfusion—involves storing the donor lung in conditions that mimic the body: the lungs are ventilated, maintained at normal body temperature and a fluid is circulated through the lung’s blood vessels (follow this link to watch a video of the ex vivo lung perfusion technique).
Recently, Dr. Keshavjee’s team demonstrated that a detailed examination of the fluid circulated through the lung could reveal which lungs may be less suitable candidates for transplantation. After four hours in the ex vivo system, researchers detected high levels of two proteins—interleukin-8 and growth-regulated oncogene-α—in the fluid of lungs that performed poorly after transplantation.
“We hope that measuring the levels of these proteins during ex vivo lung perfusion will allow clinicians to safely expand the current donor pool and improve outcomes after lung transplantation” says Dr. Keshavjee.
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Toronto General & Western Hospital Foundation. M Cypel holds a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Lung Transplantation.
Protein expression profiling predicts graft performance in clinical ex vivo lung perfusion. Machuca TN, Cypel M, Yeung JC, Bonato R, Zamel R, Chen M, Azad S, Hsin MK, Saito T, Guan Z, Waddell TK, Liu M, Keshavjee S. Annals of Surgery. 2015 March. [Pubmed abstract]




Comments